Explain the Difference Between Intracellular and Extracellular Transport
I think you mean to say intracellular versus extracellular. The voltage charge difference between the intracellular and extracellular fluid when the cell is at rest ie not depolarised by an action potential.
Difference Between Intracellular And Extracellular Fluid Definition Types Function
The key difference between intracellular and extracellular fluids is that the fluid inside the cell is intracellular fluid while the fluid outside the cell is extracellular fluid.

. Therefore it constitutes a barrier against the movement of water and water-soluble substances between the extracellular and intracellular compartments. Q-What are the major transport mechanisms for CO2. As adjectives the difference between extracellular and intercellular is that extracellular is occurring or found outside of a cell while intercellular is located between or connecting cells.
Intracellular enzymes may be present freely in the cytoplasmic fluid of the cell or they may be bound to some organelles such as ribosomes. Also found in the ICF are cellular. Mechanisms responsible for the resting membrane potential.
What is the difference between intracellular and extracellular digestion. Blood plasma is the second part of the ECF. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life.
Target cells have receptors. In Parameocium Amoeba root hair cells of many plants and WBCs in animals transportation of materials occurs within the cell due to the streaming movement of the cytoplasm known as cyclosis. Endocytosis is defined as the uptake of material by the invagination of the plasma membrane.
In this article we will discuss intracellular and extracellular enzymes with the help of various examples. Science Nursing QA Library Explain the difference between extracellular and intracellular fluid. 3Active extrusion of Na is important for osmotic reasons.
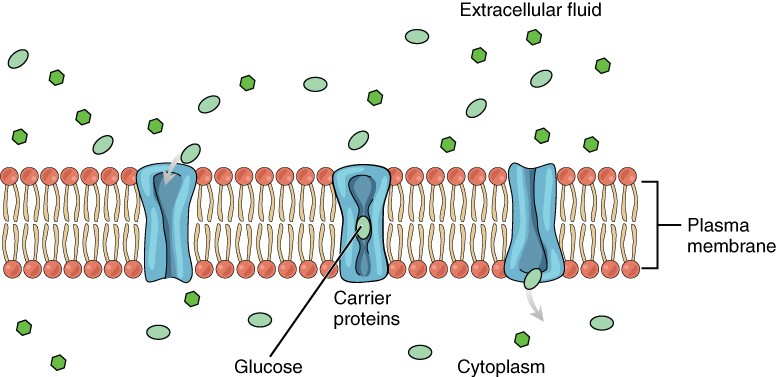
Intracellular digestion refers to nutrient processing and absorption that occurs inside of cells within special structures. Explain the differences between intracellular and extracellular fluids in relationship to intake and output 2. They additionally have a hydrophilic channel through their core that provides a hydrated opening through the membrane layers.
Extracellular bacteria can be pathogenic because they induce a localized. While glucoses essence as the holy grail may be debatable glucose undeniably serves as an essential energy source for our bodies. Organelles like the nucleus endoplasmic reticulum mitochondria lysosomes and Golgi apparatus are suspended in and supported by the ICF.
A cell membrane surrounds the cell separating the cell interior and external environment. Cells release signaling molecules to target cells and communicate with each other via signaling molecules in multicellular organisms. As the name indicates such enzymes are present inside the cell membrane.
The intracellular fluid ICF is the fluid within cells. Resting membrane potential. The interstitial fluid IF is part of the extracellular fluid ECF between the cells.
Intracellular Digestion Digestion that occurs inside our cells literally in the cytoplasm Extracellular Digestion Digestion that occurs outside our cells. Adjective - occurring or found outside of a cell. Both cell interior and exterior have to be in ideal.
Adjective head Located between or. Explain the basis for the different types of inflorescence in flowering plants. Chemical gradients generated by active transport pumps.
The humoral immune response is the main protective response against extracellular bacteria. This is known as intracellular transport. One very well understood form of intracellular transport is known as endocytosis.
Q-Define the term inflorescence. Requires direct or indirect use of energy. Potential - electrical gradient created by active transport of ions across the cell membrane is a form of potential energy just as concentration.
Q-Describe the events taking place during interphase. The greater the difference in concentration the more rapid the diffusion. Q-Explain why pure water has the maximum water potentialExplain why pure water has the maximum water potential.
What is its connection and diseases in human What is its connection and diseases in human Explain the difference between extracellular and intracellular fluid. Extent of the concentration gradient. However lipid-soluble substances can penetrate this lipid bilayer diffusing directly through it.
More specifically eukaryotic cells use endocytosis of the uptake of. Channel proteins have hydrophilic domains exposed to the intracellular and extracellular fluids. 2Gradients for Na and K concentrations across the plasma membranes of nerve and muscle cells are used to produce electrochemical impulses ex.
Explain which routes are most effective for the older adult patient fluid. Intracellular Fluid ICF The fluid inside of cells also called the cytoplasm or cytosol makes up about 60 of the water in the human body totaling about 7 gallons. Explain the difference between a chemical gradient an electrical gradient and an electrochemical.
Intracellular transport is an overarching category of how cells obtain nutrients and signals. The main difference between intracellular and extracellular digestion is that intracellular digestion occurs inside the food vacuoles within the cell whereas extracellular digestion occurs outside the cell in the lumen of the alimentary canal. Intracellular digestion is breakdown that occurs inside of cells.
The lipid bilayer is not miscible with either the extracellular fluid or the intracellular fluid. Materials travel between cells and the plasma in capillaries through the IF. The concentration of ions are significantly different.
Distinguish between active transport and passive transport. The key difference between intracellular and intercellular signaling is that intracellular signaling is the communication within the cell while intercellular signaling is the communication between cells. Electrical disequilibrium or electrical gradient between the extracellular fluid and the intracellular fluid resting - the membrane potential has reached a steady state and is not changing.
The antibodies act in several ways to protect the host from the invading organisms including removal of the bacteria and inactivation of bacterial toxins Figure 17-8. A molecule that moves freely between the intracellular and extracellular compartments is said to be an _____ solute. Welcome our holy grail glucose.
Antonyms intracellular intercellular. In roundworms there are no blood vessels and the body fluid. 1Steep gradient provides energy for coupled transport of other molecules.
What are the most common routes used to influence the correction of fluid imbalances in patients. View the full answer. Extracellular digestion is the breakdown of food in spaces external to any cells as in the intestines.

Body Fluids And Fluid Compartments Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Body Fluids And Fluid Compartments Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Difference Between Intracellular And Extracellular Fluids Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
What Is The Difference Between Intracellular And Intercellular Fluid Quora
Comments
Post a Comment